How to choose a validator for staking – 101
Staking has become a cornerstone of blockchain ecosystems, offering participants the chance to actively contribute to network security and governance, while earning rewards and airdrops. In the Cosmos Ecosystem, staking is crucial for maintaining a chain’s integrity and functionality. This article gives an overview of the essentials of staking, airdrops, the role of validators, and selecting the right validators within the Cosmos Ecosystem.
What is Staking?
Staking in blockchain refers to locking up coins or tokens in order to support network security, including transaction validation and block creation. Most of this work is actually handled by validators, who charge a certain amount of commission. Stakers only have to choose which validator they want to stake their coins with. As a staker, you can earn rewards and receive the right to vote on governance proposals.
What are Validators?
Validators are special actors in a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchain like Cosmos. They validate transactions, propose new blocks, and ensure network consensus and security. Their role in preserving the decentralized nature of the blockchain is foundational, confirming transaction legitimacy and safeguarding against malicious activities.
What are the most important roles of Validators:
- Transaction Validation: Validators ensure that only legitimate transactions are recorded on the blockchain, maintaining network integrity.
- Block Proposal: Based on a rotational system, validators propose new blocks and choose which transactions are included into the next block.
- Network Security: By staking tokens as collateral, validators have a vested interest in the network’s security, deterring malicious behavior.
- Governance Participation: Utilizing their delegated voting power in governance, validator’s votes on proposals have a big influence on the network’s protocol and future direction. Validators are voting on behalf of their delegators, but delegators can overrule their validator’s decision by casting a different vote themselves.
Decentralization and Voting Power:
A relatively even distribution of voting power is important for network liveliness and security.
All chains in the Cosmos Ecosystem are based on the CometBFT (ex. Tendermint) consensus algorithm. In this consensus model, which was developed by J. Kwon and E. Buchman, 2/3 of the network’s total voting power are needed to reach consensus. This essentially means that “a validator controlling over 66.67% of the voting power has full control over the chain and can do whatever they like”. It is the delegator’s duty to prevent this scenario from happening. By delegating your tokens to a validator you directly influence that validator’s voting power, and therefore your delegation has an effect on the network’s security, liveliness, and political future.
What are the risks connected to all of that?
As long as everything works as expected, validators are honest and the chain makes block after block, everybody is happy. But if enough validators fail to provide a block signature (>1/3 of voting power) the chain halts until the 66.67% goal is reached again. This impacts blockchain liveliness and therefore validators are punished for bad uptime.
There’s another case that’s even worse: a validator could try to forge a malicious block. In practice an attacking validator can’t just “propose” a wrong block, because it wouldn’t be confirmed by the other validators. To attack a blockchain, a malicious validator would need to “propose the good and the bad block simultaneously”, essentially confusing other validators and tricking them into accepting the bad block. This is called “double-signing”, and it’s the worst thing a validator could do.
There are various punishments for delegators of misbehaving validators:
- Liveliness misbehavior / Uptime fault: “soft slashing” > jailing of the validator
If the validator fails to sign a certain amount of blocks in a given time window, it will be “jailed” and removed from consensus, preventing it and its delegators from earning further rewards. Depending on chain configuration, uptime faults can also result in “soft slashing” of all delegated funds of the respective validator. On most chains the “soft slash fraction” is set to 0% or 0.1%, which gets greatly outweighed by the staking reward in most of the cases. So if your validator goes to jail for inactivity you risk this 0-0.1% of your stake, and to miss out on rewards until the validator comes online again.
As soon as the validator has resolved the incident and has ensured that their node is synced, they have the power to “unjail” themselves by simply sending a unjail transaction.
- Byzantine misbehavior / Double sign fault: “hard slashing” > tombstoning of the validator
First of all: double signings don’t happen very often. And to our knowledge the whole of the Cosmos Ecosystem has not yet seen a double signing incident that was actually a prevented attack by a malicious validator. Each and every incident that has happened was related to operational error. Validators are different to web2 infrastructure when it comes to maintenance: you can’t just spin up a redundant validator because then you would double sign. For this reason validator node maintenance and failover procedures have to be carefully planned, operators need to be very experienced.
If a validator double signs it is also removed from consensus (“jailed”), but they can never unjail themselves in contrast to getting jailed for liveliness faults. This is called “tombstoning” because it renders that validator key unusable, and the validator can never become part of consensus again. On most of the chains in the Cosmos Ecosystem the “hard slashing” fraction for byzantine misbehavior is set to a hefty 5% slash of all delegated coins to the affected validator.
“No risk no reward” is what they say, and this is very true when it comes to delegating your cryptographic assets. So choose your validators wisely.
How to Choose Validators:
As we have now discussed, selecting the right validators is a crucial decision for Stakers, impacting the network’s security and reliability. Here are some factors to consider:
- Performance History and Uptime: Research the validators’ past performance for reliability, high uptime and efficient block production. A high uptime indicates a smaller amount of missed blocks. Beware that 100.00% uptime doesn’t necessarily mean that the validator is exceptional. In fact, the implementation of more rigorous security measures introduces more latency, which means “more secure validators might miss a block more from time to time”.
- Self Delegation: Validators HAVE to stake to themselves, which is called “self delegation”. Validators with more at stake are incentivized to act in the network’s best interest. In many cases a validator’s reputation is worth far more than their self delegation at risk.
- Voting Power: Diversifying your stake, especially by delegating to validators outside the top ten, can help prevent the concentration of voting power and empower new contributors. This is crucial for maintaining a balanced and decentralized network. Validators with excessive voting power can have a bad impact on the network’s security and governance outcomes. By supporting smaller or newer validators, you do not only contribute to a healthier, more resilient network, you also have the power to incentivize various ecosystem contributions by these often smaller teams.
- Community Engagement: Validators that actively engage with the various communities help to increase the total ecosystem reach and information availability, contribute to discourse and improve overall morale and vibe. Be on the lookout for validators with a positive presence in community forums and on social media.
- Security: Research your validator’s security measures. A good validator should be public about their security best practices, infrastructure and organizational / team structure.
- Slashing History: Try to research if your validator has been soft- or even hard-slashed before. Some block explorers show the number of times a validator has been jailed. Is your validator publicly acknowledging incidents and publishing reports if something went wrong? Even better, then you know that they are fully transparent about their operation and you can be pretty sure that they will try the best to prevent the same scenario from happening again.
- Commission Rates: The commission rate is the percentage of the accrued staking rewards that are paid to the validator for their services. If you are in fact still reading this article you will have a pretty good understanding about the complexity of a reliable validator operation. Ensuring a reliable and secure validator operation is quite costly. Choose validators whose rates align with your preferences and ensure they provide fair value for their services. Usually the commission rate should be somewhere between 5% and 10% (more or less). 0%-commission validators offset their cost and cover it with the income of other chains or products. They are often excluded from airdrops because they promote stake centralization.
- Exchange Validators, Custodial Validators: Centralized Exchanges sometimes offer their customers to directly stake tokens on their platform. Of course they choose their own validators for that (Looking at you, Binance). Because many crypto users still hold most of their coins on CEXs this system leads to drastic centralization of stake and governance voting power. Do we want CEXs to have most of the responsibility in our ecosystems? Obviously not. And this is also the reason why CEX and VC validators are generally excluded from most of the airdrops.
For validators in the Cosmos ecosystem you can find most of the information mentioned above on Mintscan. Like this validator overview for Osmosis: https://www.mintscan.io/osmosis/validators
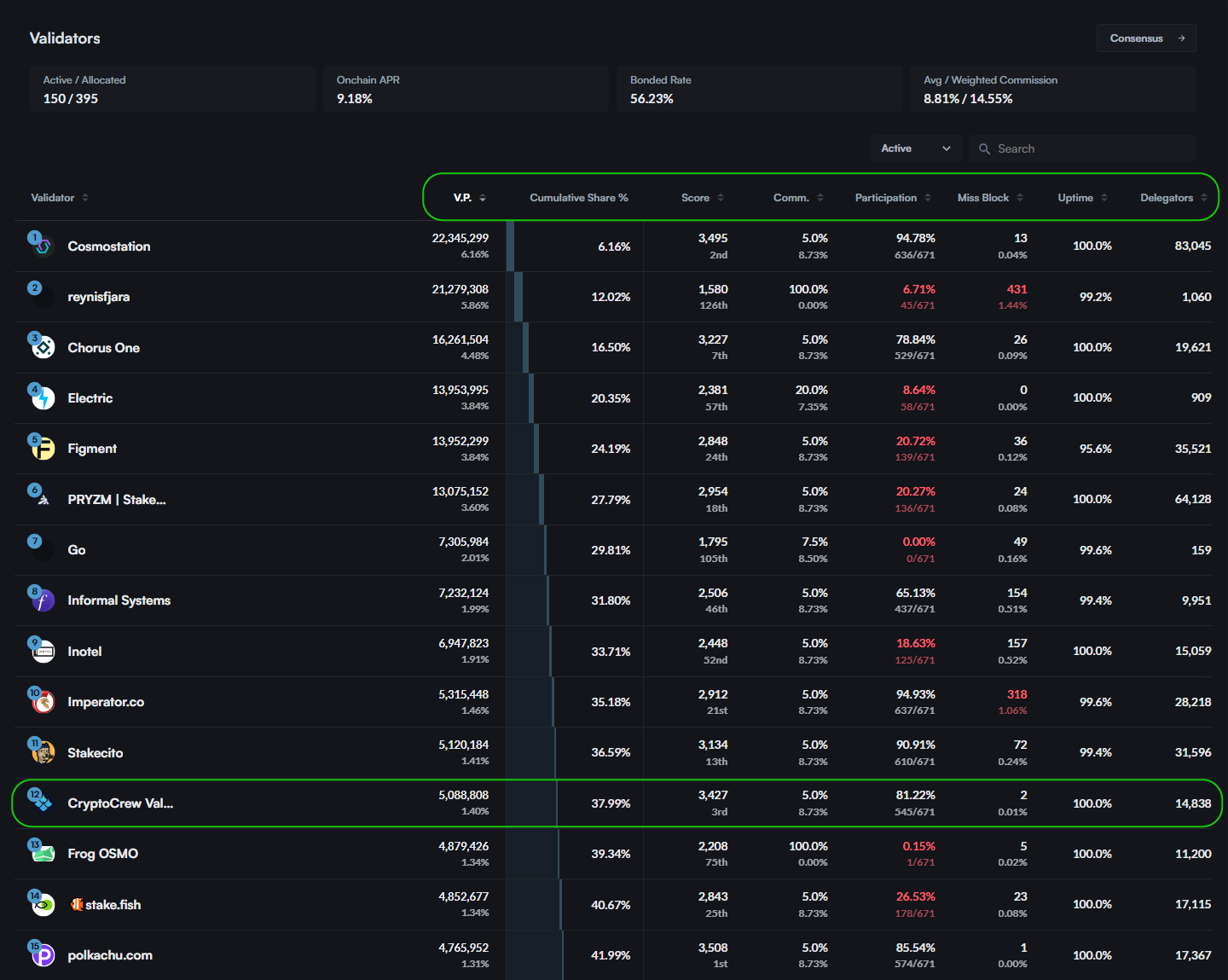
Validators for Osmosis on Mintscan
If you click on one validator in the list, you get an even more detailed overview:
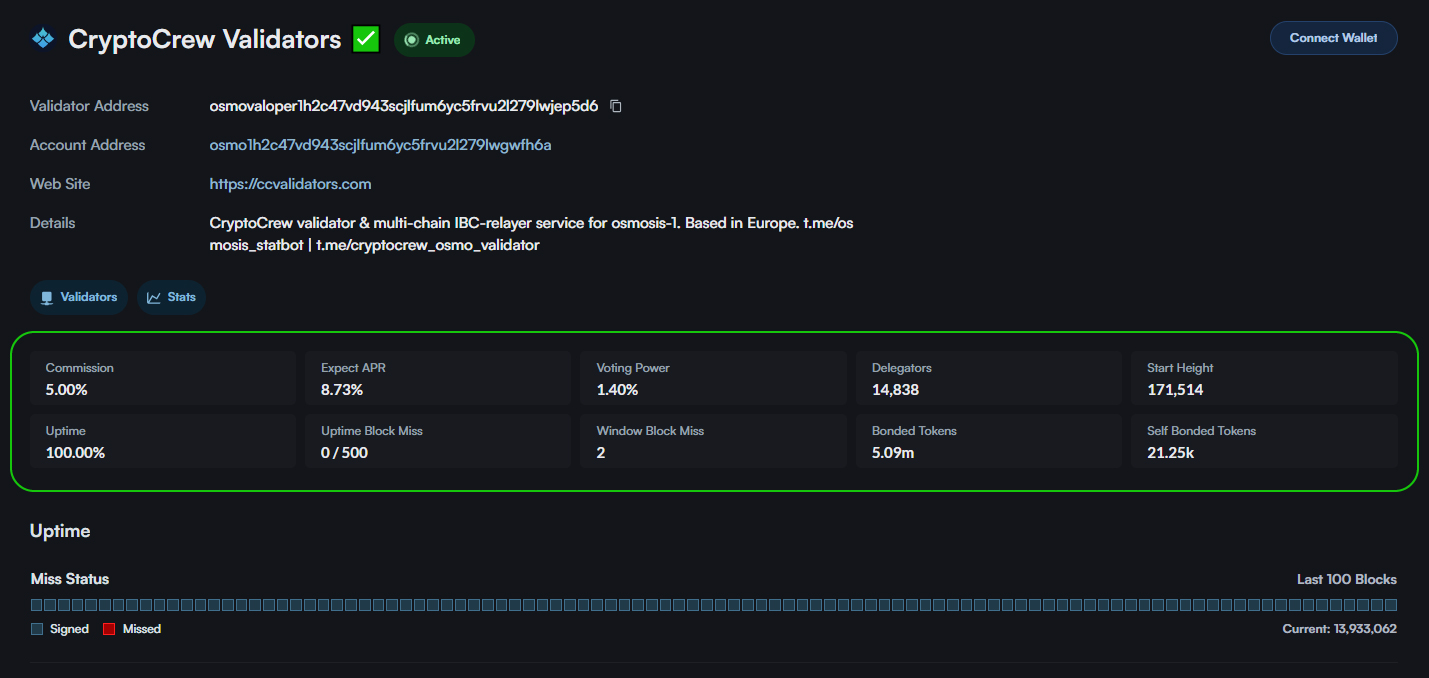
CryptoCrew Validators on Osmosis
What’s the concept of Airdrops?
Those who delegate their coins to validators might find themselves eligible for airdrops for emerging chains or projects. This process often includes a snapshot mechanism, which essentially means holdings of each account are recorded at a given block. It is the airdropping team’s decision how the airdrop is designed and executed. Consequently, delegators may receive token rewards proportional to their staked amounts.
Best Practices for Validator Selection:
- Use on-chain and off-chain data to determine your own validator score.
- You can also use general staking information platforms such as stakingrewards.com.
- Always distribute your stake between multiple validators to decrease slashing risk. If you have delegated all your stake to one validator, all your stake gets slashed if that validator misbehaves.
- Try and get to know your validators – meet them on social media or at events and find out which value they provide.
Conclusion:
Staking in general extends beyond earning rewards. As a delegator you are an active citizen of a blockchain network. You support network security and have a say in the future of the project. By understanding validator roles and making informed choices, you can contribute to a robust, decentralized blockchain ecosystem.
Relevant links:
https://ping.pub/cosmos/uptime.
For real-time monitoring of CryptoCrew Validators uptime, you can visit our live validator uptime dashboard at https://uptime.ccvalidators.com/.
To gain insight in certain validator and network metrics you can also take advantage of the Advanced Staking Dashboard on https://ccvalidators.com/#calculator.
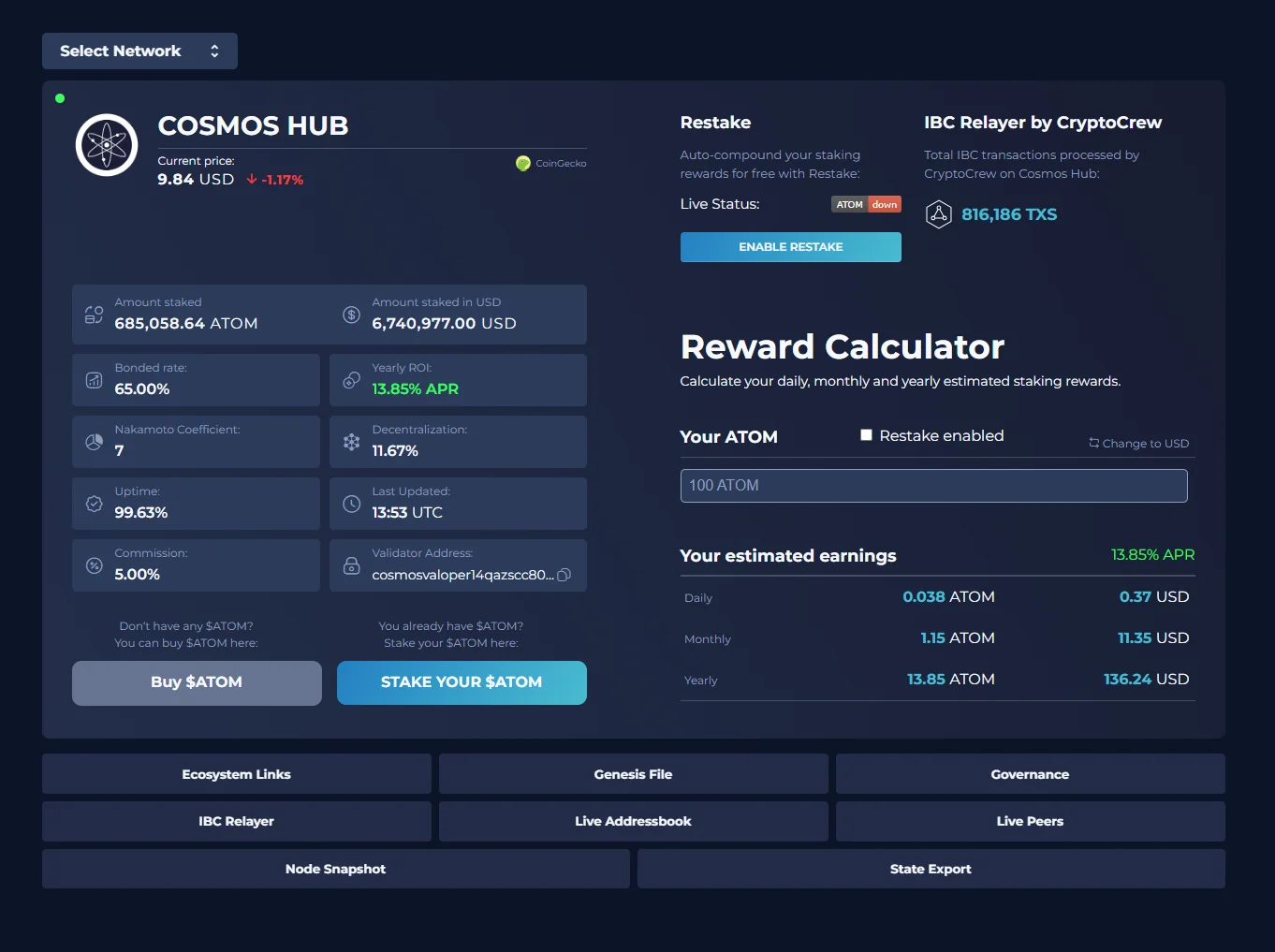
CryptoCrew Staking Dashboard
That’s a wrap!
—
Find our social media links (X, Telegram, Reddit, etc.) and engage with our community. We welcome your participation and look forward to connecting with you! Sincerely, CryptoCrew Validators.
Thank you very much for considering ✅ CryptoCrew Validators as the validator of your choice! We very much appreciate your trust and hope to meet you on our social media channels:
CryptoCrew Validators X: https://twitter.com/crypto_crew
CryptoCrew Validators Telegram: https://t.me/cryptocrew_validators
CryptoCrew Validators Reddit: CryptoCrew Validators (reddit.com)
Disclaimer: This article is for experienced users of blockchain technology and was written for educational purposes only! It should not be considered as advice to trade or purchase cryptocurrency. Platforms and tools mentioned in this tutorial are dedicated to users with advanced knowledge regarding blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies! The responsibility to securely store your keys, protect your crypto wallet and be safe lies solely with yourself / the user. CryptoCrew Validators and its partners will NEVER reach out and ask for your private keys – please be very careful and educate yourself in regards of your financial safety! Please store your keys safe and don‘t fall for scammers!