XION’s Generalized Abstraction – 10X Improvement for Crypto Users?
The future of cryptocurrency user experience (UX) is abstraction. Despite promising to revolutionize culture and finance, digital assets face a number of serious pain points. Blockchains (particularly outside of the Cosmos ecosystem) are still largely siloed by liquidity, wallet functionality, and application availability. Private keys are still permanently fixed to their associated addresses, the compromise of which can mean devastation for any cryptocurrency user. The array of available wallets is dizzying and making sure the right gas tokens are on the right chains can be downright infuriating.
Abstraction is the the key to addressing many of these issues and the XION network is preparing to lead the charge. In this article we’ll explain
- What is abstraction?
- What is XION’s Generalized Abstraction framework?
- How could it solve key issues in crypto UX?
Let’s dive in.
Abstraction
In software engineering, abstraction is the idea that complexity should be hidden from the users as long as functionality is not affected. Currently, across all crypto ecosystems, users who discover an app they would like to use need to consider
- What blockchain it is deployed on
- What gas token they need to use it
- Where their funds are stored
- what wallet they need to use
and so on. Every single one of these challenges could be sufficiently confusing for the user to give up and not bother using the application at all. the Generalized Abstraction framework outlined in XION’s whitepaper is likely a roadmap for all crypto applications and ecosystems to follow and it includes processes for abstracting away confusing elements like accounts, wallets, payments, fees, and more. Let’s walk through a hypothetical user’s first experience with a Web 3 application, some of the issues they might have to face in a typical user flow, and how XION’s framework aims to resolve these issues.
Discovery
Let’s imagine that our user want to try out an application, recommended by a friend of theirs. It could be a Web 3 gaming app, or an NFT marketplace, but let’s imagine that they’ve never used crypto before. They will need a wallet, but let’s imagine the friend (as a crypto native) gave some simple instructions:
- Download the wallet
- Make an account
- Use the app
Sounds straightforward. The wallet gets downloaded easily enough, and as soon as they go to make an account they are confronted with the instructions related to their private key. Ah. The friend did not warn them about public / private keys, self custody, hot vs cold wallets, and so on. At this stage, they either push through, or give up. Even if they push through, they may not understand the importance of storing the private key safely, and may end up losing access to their assets at some point in the future.
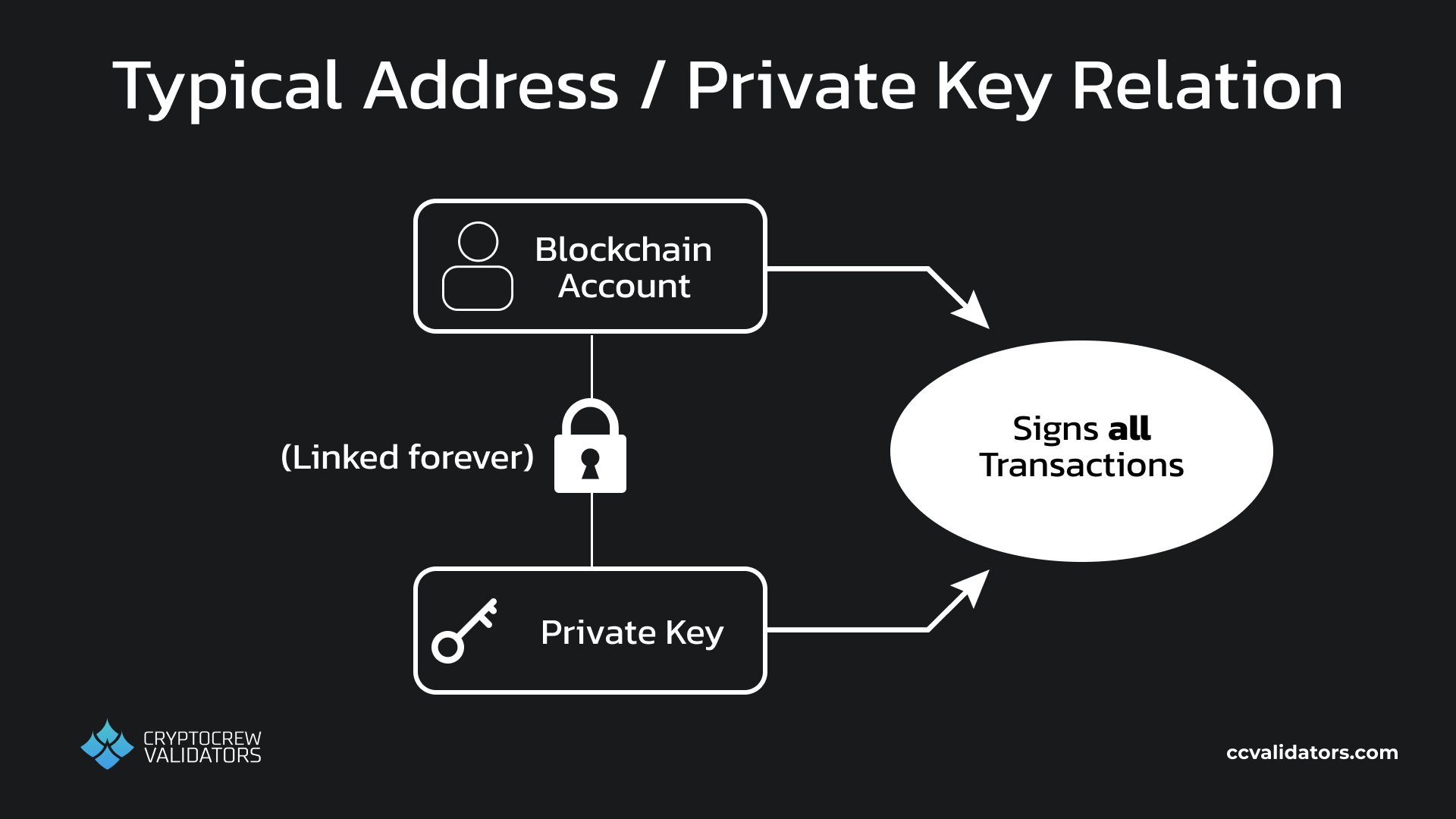
Standard blockchain addresses & private keys
XION solves this by implementing ‘meta accounts’. These accounts are actually smart contract accounts (SCA), but unlike normal smart contracts, these ones are controlled by authenticators. They allow for our user to create their first crypto account with authenticators like a familiar e-mail or biometric login, and later create dedicated private keys (another kind of authenticator) for it. It also allows for any authenticator, including the private keys, to be removed, added, or swapped out for new ones.
Each authenticator can also be paired with rule sets for even greater security. For example, you could set it up such that a hardware private key is required for IBC withdrawals from XION, but only an-in browser hot key is required for small trades on a XION DEX. Sunny Aggarwal covered the power of authenticators and rules in his Cosmoverse 2023 talk for those interested in more details.
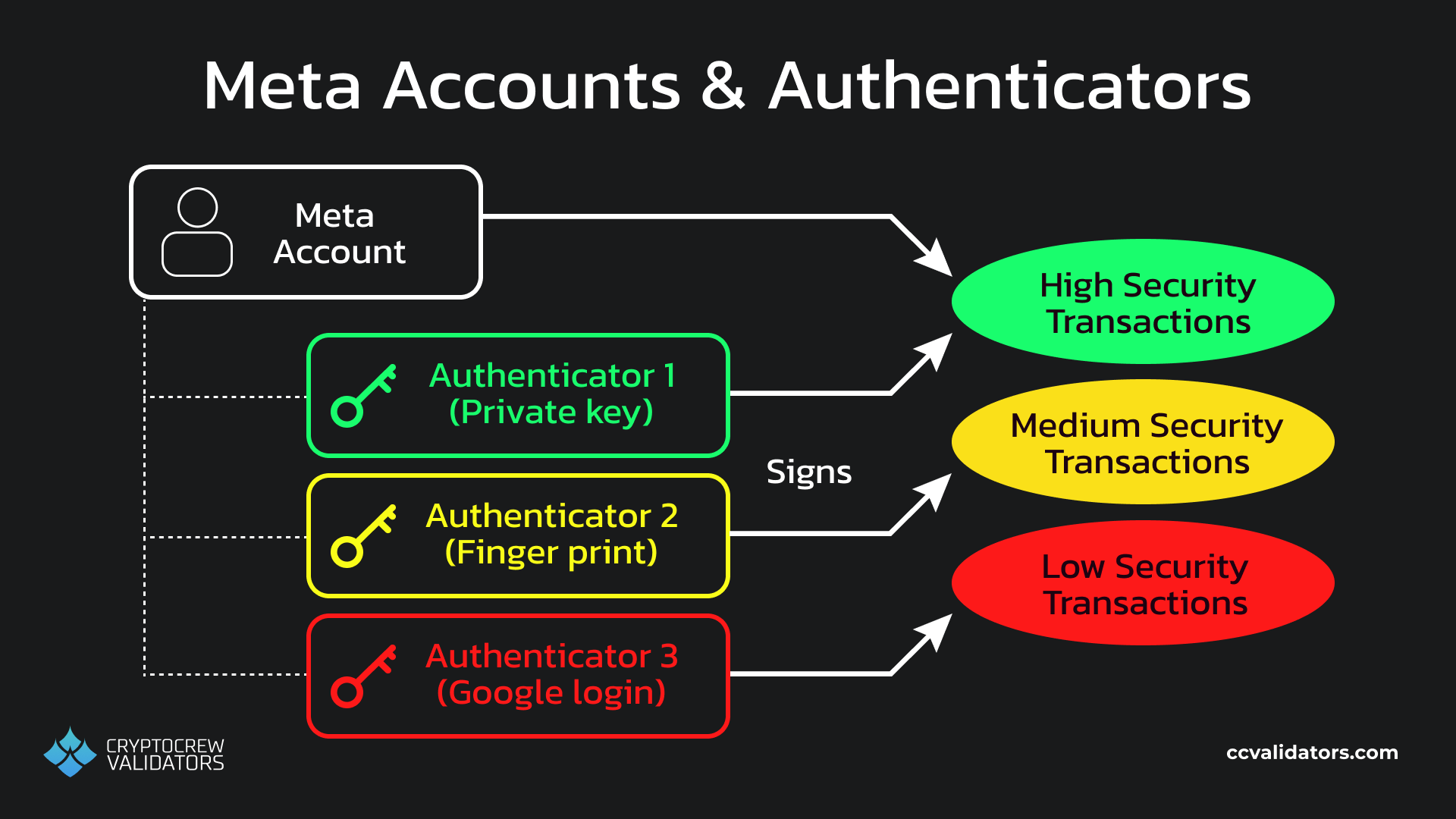
Meta Accounts & authenticators
In addition to this, XION’s signature abstraction enables up to 256 different authenticators to be added to a single meta account. Among these, users can select from multiple different public / private key pairs across different cryptographic curves. Since these can be added or removed, XION smart accounts have ‘future-proofed’ themselves against any potential changes in cryptographic security.
Interaction
Now our user has an account, and they are excited about interacting with the application. On most blockchains, they will again be confronted with an issue: You need gas tokens to initiate transactions. To move forward, our user needs to know three pieces of information:
- What blockchain is the application deployed on?
- What fee token does it accept?
- How can they own these tokens and get them in the right place?
None of these might be made obvious by the application in question, and this is not unreasonable. The user should not need to care about these details. To ease this tension, XION utilizes the fee abstraction module, which allows transaction fees to be paid in tokens other than the native XION token. In the background, this module swaps non-native tokens paid as fees for XION tokens which are then forwarded to the XION validators. Periodically, when its supply of XION runs low, it sends the foreign token balances to the Osmosis decentralized exchange over IBC where they are swapped for more XION, and returned to the module.
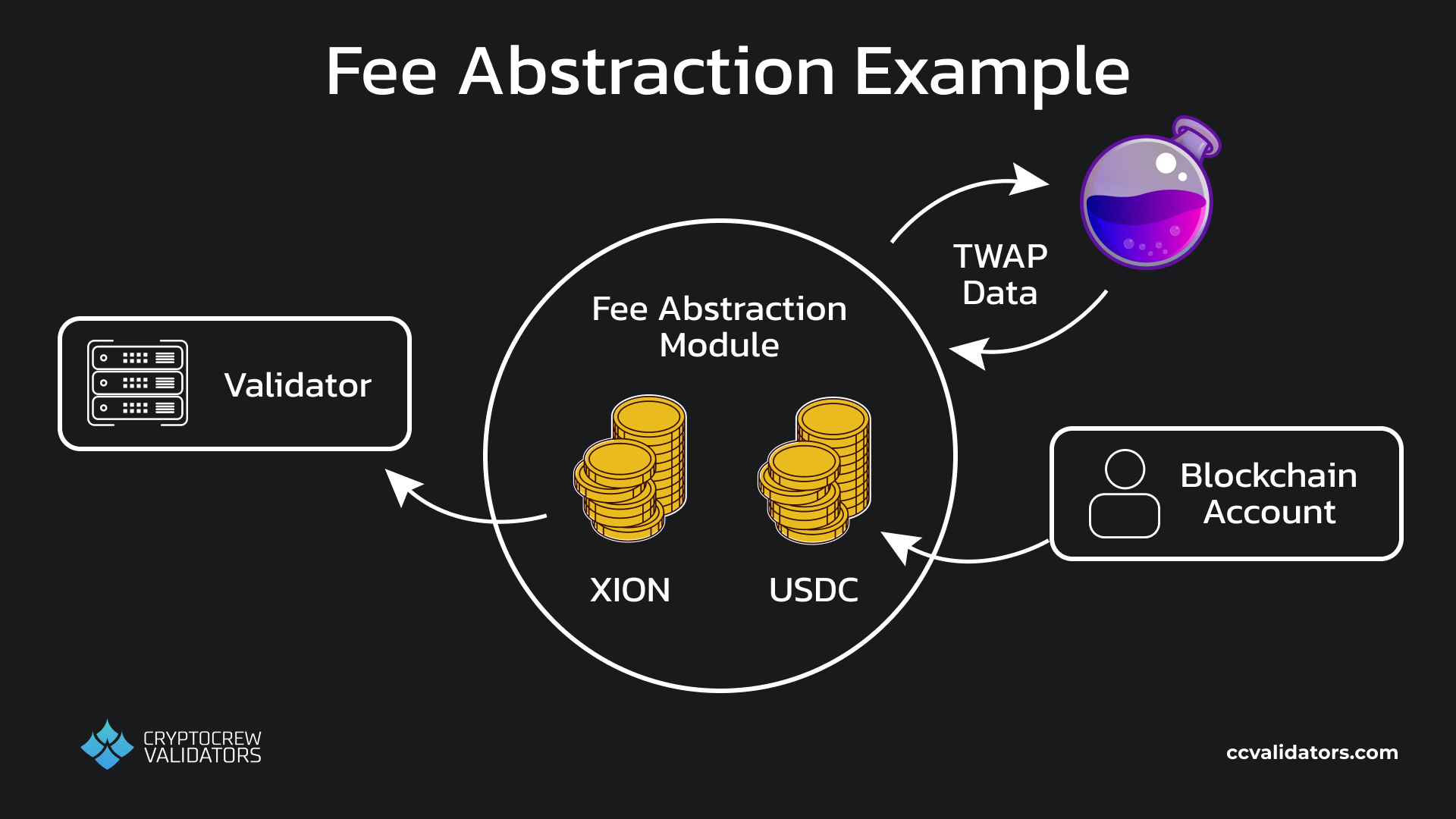
Fee Abstraction Module
As long as the user can get any accepted token onto their XION meta account, they will be able to interact with their intended application and any others in the XION ecosystem.
Expansion
Now that our user has gotten used to using a Web 3 wallet, interacting with applications, signing transactions, and managing their own custody, they may want to go out and try applications in other ecosystems and on other blockchains. For this to be a seamless experience, XION needs to support interoperability solutions so that users do not have to start from zero when they move to new chains.
The first level of this is XION’s wallet agnosticism. This means that many different wallets can be used to interact with applications built on XION, and it also means that users not need to get new wallets every time they switch chains. But even having avoided new wallets, users are still faced with tokens potentially being stuck on the wrong blockchains for interactions with their newly discovered dapps. To solve this, we need bridging.
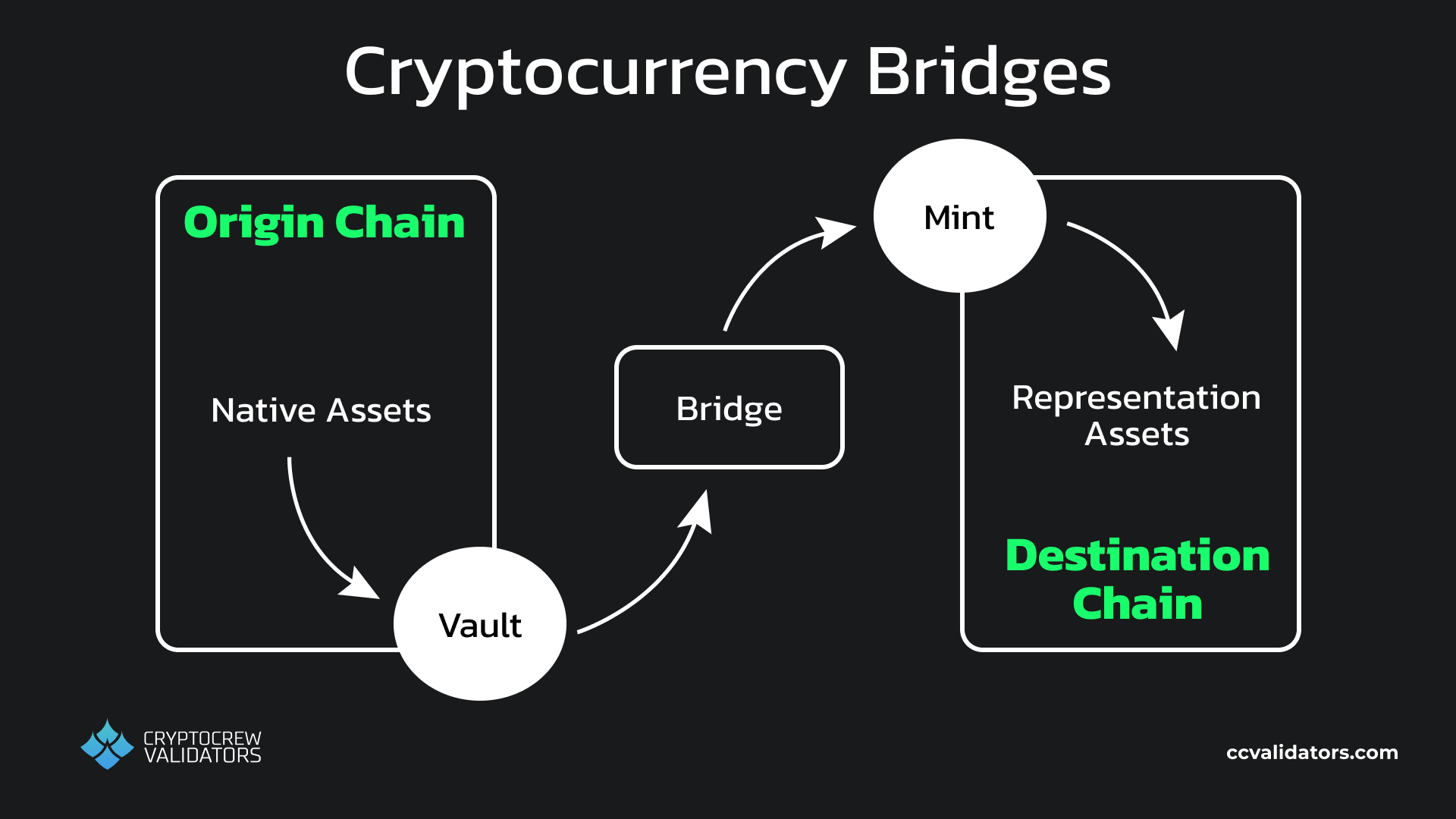
Cryptocurrency bridge structure
The XION blockchain is constructed from the Cosmos SDK (software developer kit) and is IBC enabled by default, so bridging tokens and interactions with other chains in the Cosmos is both simple and secure. It also features the packet forward middleware module so that tokens from across the Cosmos can flow easily in and out of XION with different destination chains.
For chains without IBC enabled, other bridges will need to be employed. Axelar is a long-standing bridge connecting IBC chains with Ethereum and with the recent implementation of IBC Eureka, Ethereum is now connected to the Cosmos ecosystem via IBC for the first time. Other bridging solutions will need to be implemented to connections to other popular ecosystems like Solana, The Open Network (TON), Avalanche, and others.
What makes XION’s interoperability solution really interesting is actually the combination of meta accounts and bridges. You see, the interchain accounts (ICA) module lets enabled chains create and control accounts on other chains through IBC. The problem is that you need dedicated IBC channels for these connections, and these channels can only connect smart contracts or Cosmos SDK modules (not normal accounts).
BUT since all meta accounts on XION are actually smart contracts, each meta account can individually take advantage of the ICA functionality. This means that a XION user can create and control accounts on other blockchains using their existing XION account. No new wallets, no new public / private key pair, no worrying about gas tokens.
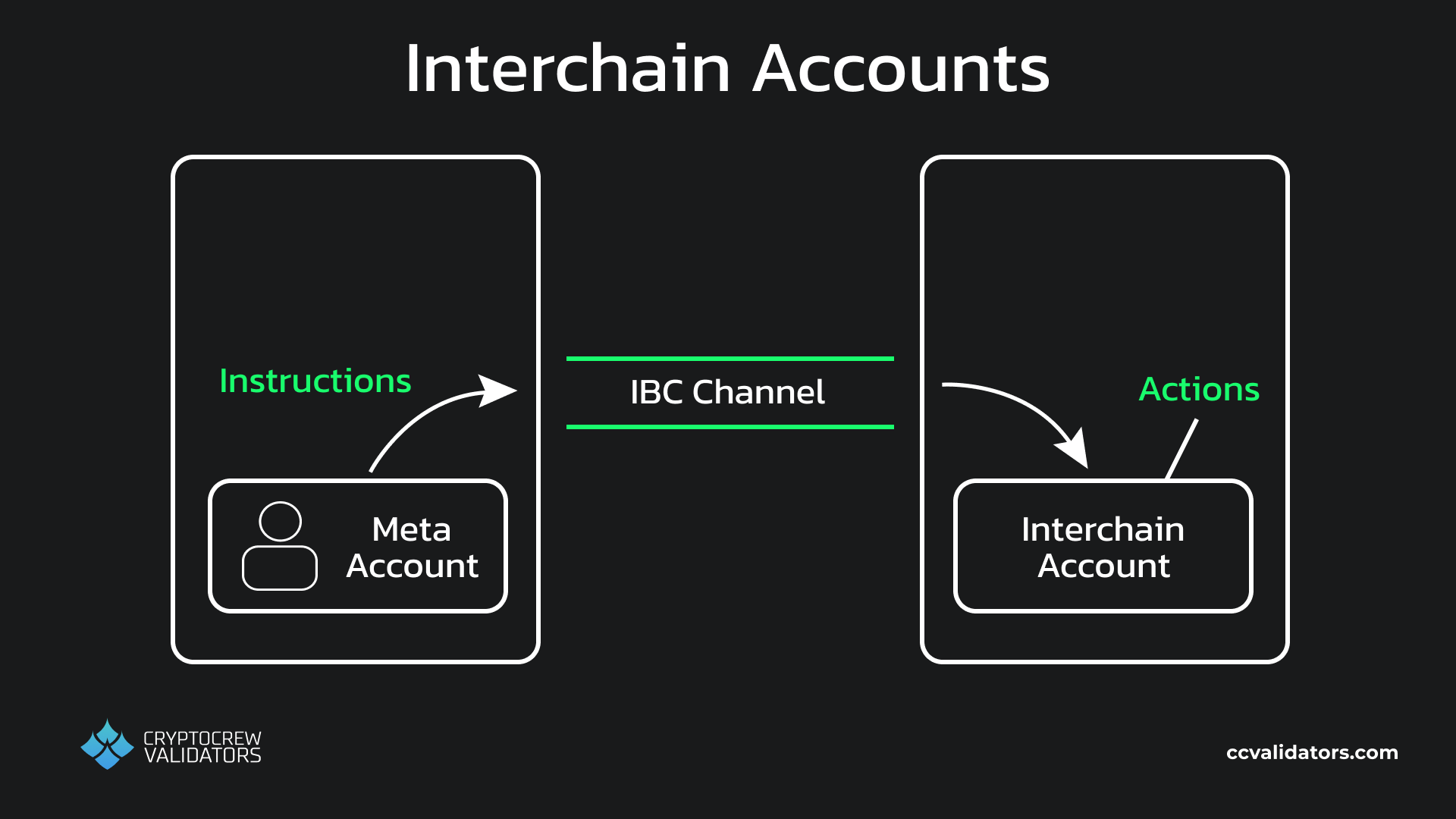
Interchain Accounts
Conclusion
XION are not the only team who have recognized that abstraction holds the key to solving many of these crypto pain points. Osmosis recently announced the Polaris application, designed to implement abstraction on cross-chain trading. Agoric’s Orchestration API has also been released on mainnet. In the Ethereum L2 world, Abstract is also working on implementing similar solutions. Much like in all important crypto narratives, abstraction is going to be an arena of fierce competition. That said, we believe that chains like XION, thinking about and assembling solutions now, are going to have a massive advantage in onboarding cohorts of new users as blockchain technology continues to mature. In the Cosmos, where native interoperability and multichain experiences are built into the foundation, we are light years ahead of other ecosystems. CryptoCrew is excited to be a genesis validators for XION and we look forward to the multichain applications that will be constructed there.
Thanks for reading!
~Robin